For the environment
- Font size
-
- Standard
- Increase
Environmental management
The Keikyu Group Basic Environmental Policy
We endeavor to preserve the global environment, reduce our environmental impact through our business and social contribution activities, and contribute to the realization of a society that can develop sustainably.
Action Guidelines
- We endeavor to make further improvements to convenience and to create appealing value along our railways, with a focus on providing environmentally friendly public transportation.
- We endeavor to reduce our impact on the environment through the effective use of resources and energy, as well as initiatives to reduce, reuse, and recycle waste.
- We endeavor to coexist with and preserve the rich natural environment along our railway lines so that our children, who will lead the next generation, inherit a better environment surrounding the railway.
- We place value on communication with all of our stakeholders, and endeavor to cooperate and work together with local communities.
- We endeavor to fully comprehend and comply with environmental laws and regulations and to increase the environmental awareness of all of our employees through awareness campaigns and educational activities.
Climate Change Countermeasures
Environmental targets
With the aim of helping to realize a carbon-neutral society, we have established long-term environmental targets. We will advance and appropriately monitor initiatives to reduce GHG emissions.
Long-term environmental target : make the Keikyu Group carbon neutral by 2050
Interim environmental target : 30.0% reduction in GHG emissions in fiscal 2030 compared with those of fiscal 2019
Disclosure Based on the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) Recommendations
We have positioned ESG initiatives as the basis of business management and pursue sustainability measures including climate change countermeasures as a matter of management strategy. In addition, we conducted analysis and disclosure based on the TCFD recommendations in June 2022 with the aim of helping to realize a carbon-neutral society. We will continue moving forward with climate change countermeasures while further increasing analysis and disclosure.
Environmental data
Environmental burden data, environmental accounting
Consolidated environmental burden data
Each of our business activities, including railway operations, requires energy and resources, and these activities also generate greenhouse gases and waste.
The Keikyu Group has set “make the Keikyu Group carbon neutral by 2050” as a long-term environmental goal, and is working to quantitatively assess and reduce the environmental impact of its business activities.
| Energy and Resource Consumption | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 |
| Light oil | 25,131 ㎘ | 18,874 ㎘ | 18,117 ㎘ | 18,779 ㎘ | 18,635 ㎘ |
| Gasoline | 879 ㎘ | 768 ㎘ | 852 ㎘ | 871 ㎘ | 746 ㎘ |
| Type A heavy oil | 487 ㎘ | 290 ㎘ | 289 ㎘ | 172 ㎘ | 133 ㎘ |
| LPG | 1,982 t | 1,474 t | 1,574 t | 1,827 t | 1,485 t |
| City gas | 6,637 ㎦ | 4,923 ㎦ | 3,188 ㎦ | 3,545 ㎦ | 3,985 ㎦ |
| Kerosene | 260 ㎘ | 233 ㎘ | 332 ㎘ | 211 ㎘ | 105 ㎘ |
| Electricity (Volume of which was electricity generated from renewable energy) |
347,649,055 kWh ( 0 kWh) |
333,294,772 kWh ( 0 kWh) |
313,640,915 kWh (12,959,350 kWh) |
309,672,593 kWh (24,996,885 kWh) |
317,884,772 kWh (27,637,800 kWh) |
| Steam, hot water, cold water | 5,963 GJ | 12,714 GJ | 11,230 GJ | 8,833 GJ | 10,342 GJ |
| Water usage *1 | 3,243,500 t | 2,169,816 t | 1,740,915 t | 1,621,882 t | 1,434,663 t |
| Copy paper purchased by offices | 159 t | 136 t | 130 t | 123 t | 132 t |
| Emissions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 |
| GHG emissions | 249,265 t-CO2 | 215,593 t-CO2 | 198,568 t-CO2 | 194,382 t-CO2 | 178,316 t-CO2 |
| Scope1 | 90,657 t-CO2 | 67,847 t-CO2 | 64,226 t-CO2 | 65,824 t-CO2 | 64,124 t-CO2 |
| Scope2 | 158,607 t-CO2 | 147,746 t-CO2 | 134,342 t-CO2 | 128,558 t-CO2 | 114,191 t-CO2 |
| Waste | |||||
| Industrial | 97,092 t | 31,246 t | 30,551 t | 17,222 t | 30,368 t |
| General *2 (Volume of which was recycled) (Percentage recycled) |
12,751 t (6,691 t) (52.5 %) |
9,054 t (4,155 t) (45.9 %) |
8,540 t (4,477 t) (52.4 %) |
10,221 t (4,356 t) (42.6 %) |
7,650 t (4,434 t) (58.0 %) |
- *Reference: Greenhouse Gas Emissions Calculation and Reporting Manual, Ministry of the Environment
- *Decimals are rounded down to the nearest whole number.
- *1Tap water, underground water (including hot spring water), ocean water
- *2Subject to the amount reported to the municipality
Nonconsolidated environmental accounting (Fiscal 2023 Results)
Environmental accounting is a system for recognizing the costs incurred as a result of environmental preservation activities as well as the effects of such activities. It also provides a framework for measuring and communicating this information as quantitatively as possible.
We have been using environmental accounting and disclosing information based on this system since fiscal 2008.
| Classification | Capital Investment | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Area Costs | |||
| Pollution prevention costs | Prevention of air, water pollution, prevention of noise, odor, and land subsidence | 396,213 | 295,009 |
| Global environment preservation costs | Prevention of global warming and conservation of energy | 235,664 | 9,160 |
| Resource recycling costs | Water and waste disposal and recycling and other resource recycling | 186,740 | 121,208 |
| Subtotal | 818,617 | 425,377 | |
| Management Activity Costs | |||
| Upstream and downstream costs | Green purchasing and procurement | - | 30,812 |
| Management activity costs | Environmental management and disclosure and enhancement and establishment of greenery areas within premises | - | 186,565 |
| Community activity costs | Participation in and donations to community activities | - | 5,119 |
| Subtotal | - | 222,496 | |
| Total | 818,617 | 647,873 | |
Basic Elements of Environmental Accounting
- Calculations are based on the 2008 edition of the Private Railway Business Environmental Accounting Guidelines.
- The scope of calculations is Keikyu Corporation on a nonconsolidated basis.
- Figures of less than ¥1,000 have been rounded.
- Only initiatives that can be reliably identified are included in the environmental accounting.
- Depreciation has not been included in the costs.
Environmental initiatives
Energy-saving measures
Introducing energy-saving railcars
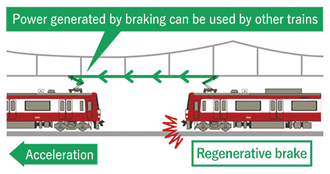
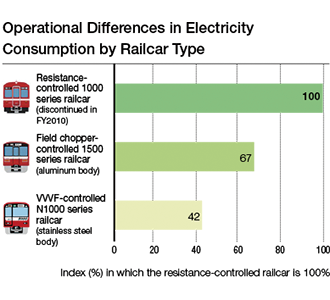
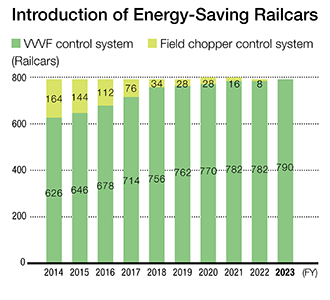
By fiscal 2010, we had discontinued all traditional resistance-controlled railcars and replaced them with energy-saving railcars equipped with regenerative brakes. In addition, we have progressively introduced variable voltage variable frequency (VVVF)-controlled railcars, which are more efficient in regenerating electricity than field chopper-controlled railcars. As of the end of fiscal 2023, VVVF-controlled railcars accounted for approximately 100% of our railcars.
Switching Railway Stations and Trains Over to LED Lighting

LED lighting
To reduce energy consumption, we are progressively converting lighting fixtures in railway stations and trains to light-emitting diode (LED) lighting.
Progress of LED conversion as of the end of fiscal 2023
Railway stations : 46.0% complete
Railcars : 68.0% complete
Electricity consumption and energy intensity of operations
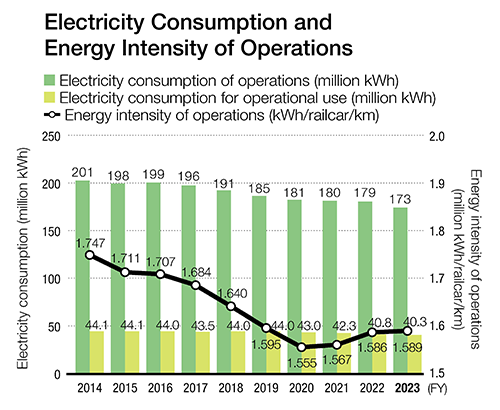
| FY | For railway operation (million kWh) | For auxiliary use (million kWh) |
Energy intensity (kWh/railcar-km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 201 | 44.1 | 1.747 |
| 2015 | 198 | 44.1 | 1.711 |
| 2016 | 199 | 44.0 | 1.707 |
| 2017 | 196 | 43.5 | 1.684 |
| 2018 | 191 | 44.0 | 1.640 |
| 2019 | 185 | 44.0 | 1.595 |
| 2020 | 181 | 43.0 | 1.555 |
| 2021 | 180 | 42.3 | 1.567 |
| 2022 | 179 | 40.8 | 1.586 |
| 2023 | 173 | 40.3 | 1.589 |
Introducing Solar Power Generation
For use in the operation of facilities, we have introduced solar power generation to some of our railway stations and Group companies.
Facilities to which solar power generation was introduced
- Haneda Airport Terminal 3 Station
- Minamiōta Station
- Kanazawa-bunko Station
- Aburatsubo Keikyu Marina
- Kamoi Driving School

Introducing Net-Zero CO2 Emissions Electricity Generated from Renewable Energy Sources

net-zero CO2 emissions
Changeover to renewable energy
- Keikyu Corporation
- Electricity consumption of the operations of the Airport Line (since 2021)
- Electricity consumption of the business operations of 19 railways stations on the Keikyu Main Line between Keikyū Higashi-kanagawa and Kanazawa-hakkei Stations and all railway stations on the Zushi Line (since 2021)
- Electricity consumption of the Keikyu Group head office, which includes the offices of 12 Group companies (since 2021)
- Electricity consumption of the business operations* of six railway stations on the Kurihama Line between Keikyū Kurihama and Misakiguchi Stations (since June 2023)
- Group companies
- Electricity consumption of Hayama Marina (since April 2023)
- Electricity consumption of certain real estate properties owned by Rinko Estate Co., Ltd. (since April 2023)
The aforementioned introduction of electricity generated from renewable energy sources reduces CO2 emissions by an amount equivalent to approximately 12,000 tons per year.
- *Railway station lighting, air conditioners, railway station equipment, railway crossings, and signals
Other initiatives to Reduce Environmental Impact
Introducing Environmentally Friendly Buses
In an effort to minimize environmental impact, Keihin Kyuko Bus Co., Ltd., has been operating SORA fuel cell buses and compact electric buses, which were introduced in 2019 and March 2023, respectively. Meanwhile, Kawasaki Tsurumi Rinko Bus Co., Ltd., has been working to reduce the burden on the environment by operating buses that use biodiesel fuel.


Introducing of EVs in the Taxi Business

The Keikyu Taxi Group has introduced 50 EV taxis* since April 2023 in an effort to reduce GHG emissions.
- *Keikyu-Kotsu Co., Ltd.: 15 EV taxis, Keikyu Yokohama Jidosha Co., Ltd.: 10 EV taxis, Keikyu Bunko Taxi Co., Ltd.: 10 EV taxis, Keikyu Hayama Kotsu Co., Ltd.: five EV taxis, Keikyu Chuo Kotsu Co., Ltd.: 10 EV taxis
Acquiring Environmental Certification in Real Estate Operations

acquired ZEH-M Oriented certification
PRIME STYLE KAWASAKI has become the first condominium in the city of Kawasaki to receive ZEH-M Oriented certification, which recognizes environmentally friendly condominiums that realize significant energy savings while maintaining the quality of indoor environments. We will continue to acquire environmental certification for future development projects.
Promotion of a Recycling-Based Society
To promote a recycling-based society, we are making effective use of finite resources and reducing waste. As a corporate group with rich marine environments in our lineside areas, we are also actively advancing initiatives to reduce ocean plastic waste.
Washing Buses with Recycled Water

In March 2019, Kawasaki Tsurumi Rinko Bus concluded an agreement with the city of Kawasaki for the use of water that has undergone advanced treatment at the Iriezaki Wastewater Treatment Center. By washing buses with water produced from the advanced treatment of sewage, we will utilize water resources effectively and help build a society based on recycling and consideration for the global environment.
Keikyu Group Plastic Waste Reduction Campaign

In 2019, we concluded an agreement with Kanagawa Prefecture on cooperation and collaboration for the promotion of the SDGs. As part of this initiative, we are promoting the Keikyu Group Plastic Waste Reduction Campaign, which is focused on reducing ocean plastic waste. Aiming to help realize SDG 14, which calls on humankind to “Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development,” the Keikyu Group is implementing a range of activities, such as conducting cleanup activities at beaches, popularizing reusable shopping bags, and introducing straws made of biodegradable materials, throughout the Group.
Biodiversity Conservation
We contribute to the conservation of biodiversity through activities to preserve the natural environment in lineside areas and through
environmentally friendly business activities.
The Miura Forest Project
Launched in February 2023, the Miura Forest Project aims to further demonstrate the capacity of these forests to absorb carbon dioxide through the sound management of the approximately 100 hectares of Company-owned forests in the Miura Peninsula, as well as create beautiful and highly functional forests that help preserve biodiversity and open up possibilities for the future.
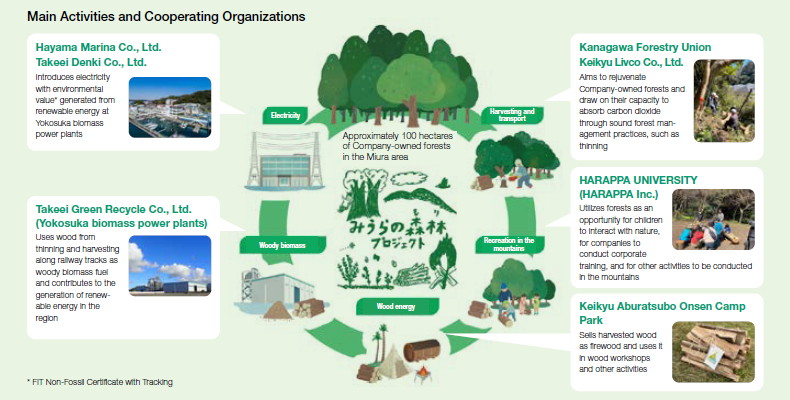
Cooperation Efforts to Preserve the Koajiro Forest

One of Miura’s irreplaceable assets, Koajiro Forest still has a natural water system as well as a valuable ecosystem that is home to rare species. As part of our cooperation in efforts to protect the natural environment, we have voluntarily preserved roughly 10 hectares of our forest and donated approximately 2 hectares to Kanagawa Prefecture in response to its designation of Koajiro as a special suburban green space preservation area.

